9. Force components
This app calculates the horizontal and vertical components of a force at a given angle.
Working app at: https://pc-force-components.anvil.app
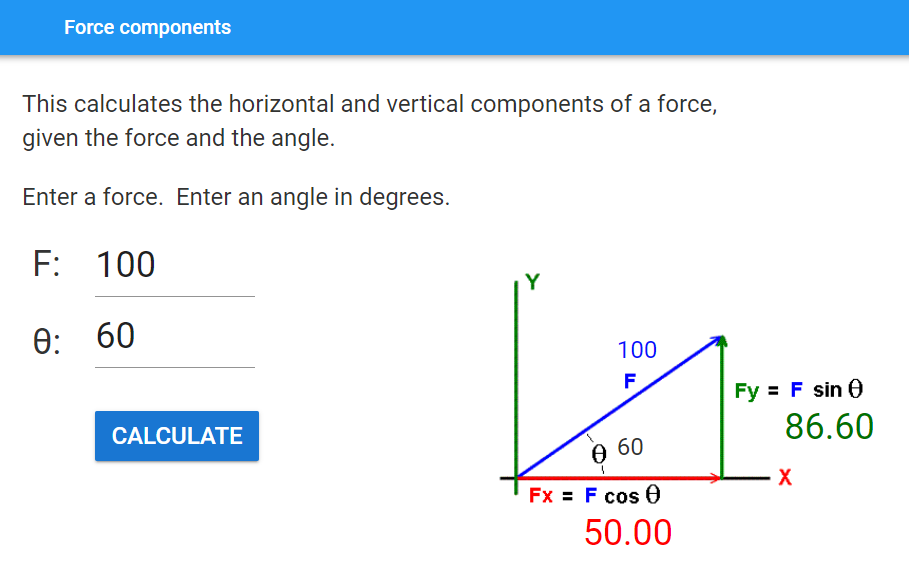
Use the image above to build the interface, using textboxes for the inputs and labels for other text fields.
Use a XY panel for the diagram region, so that the text labels can be placed over the force diagram.
Download the diagram file
force_diagram.9.1. Get started
Click: Blank App.
Choose: Material Design
9.2. Key components
Name the input textboxes: force and angle.
Set both input textbox property type settings to number.
Name the labels on the diagram: diagram_force and diagram_angle.
Name the output labels on the diagram: Fx and Fy.
Set the foreground colour of the diagram_force label to #0811fc.
Set the foreground colour of the Fy label to #007200.
Set the foreground colour of the Fx label to #ff0000.
Name the error label : error.
9.2.1. Error field
Drag and drop a label component onto the column panel below the width textbox.
In the properties panel: name section, set the name to error.
In the properties panel: text section, set the font_size to 16.
In the properties panel: appearance section, set the foreground_color to #ff0000.
In the properties panel: icon section, set the icon to fa:exclamation-triangle.

Code to hide or show error field takes the error parameter.
An error will be shown if error is a text string.
Passing None as the error parameter hides and clears the error field.
def do_error(self, error):
# check for error and display it if present
if error:
self.error.text = error
self.error.visible = True
else:
# hide error and clear it
self.error.text = ""
self.error.visible = False
9.3. Event Code
Both the clicking the calculate button and pressing enter in the input textboxes attempts to produce the output.
def calculate_click(self, **event_args):
self.do_calculation()
def angle_pressed_enter(self, **event_args):
self.do_calculation()
def force_pressed_enter(self, **event_args):
self.do_calculation()
Changing the force or angle inputs triggers the placement of those values on the diagram.
def force_change(self, **event_args):
self.diagram_force.text = self.force.text
def angle_change(self, **event_args):
self.diagram_angle.text = self.angle.text
9.4. Calculation
The input angle needs to be converted from degrees to radians for the cos and sin functions.
i.e
angle = self.angle.text * (pi / 180)Instead of importing the whole math library, the cos, sin and pi methods can be selectively imported via:
from math import cos, sin, pi.f-stings allow convenient formatting to 2 decimal places.
e.g.
self.Fx.text = f'{fx:.2f}'from math import cos, sin, pi
def do_calculation(self):
try:
# angle in degrees, convert to radians
force = self.force.text
angle = self.angle.text * (pi / 180)
fx = force * cos(angle)
fy = force * sin(angle)
except TypeError as error:
self.Fx.text = None
self.Fy.text = None
self.do_error('use positive values')
else:
if fx <= 0 or fy <= 0:
self.Fx.text = None
self.Fy.text = None
self.do_error('use positive values')
else:
self.Fx.text = f'{fx:.2f}'
self.Fy.text = f'{fy:.2f}'
self.do_error(None)
9.5. Final Code
The full code is below.
from ._anvil_designer import Form1Template
from anvil import *
import anvil.tables as tables
import anvil.tables.query as q
from anvil.tables import app_tables
from math import cos, sin, pi
class Form1(Form1Template):
def __init__(self, **properties):
# Set Form properties and Data Bindings.
self.init_components(**properties)
# hide error field
self.error.visible = False
def calculate_click(self, **event_args):
self.do_calculation()
def angle_pressed_enter(self, **event_args):
self.do_calculation()
def force_pressed_enter(self, **event_args):
self.do_calculation()
def force_change(self, **event_args):
self.diagram_force.text = self.force.text
def angle_change(self, **event_args):
self.diagram_angle.text = self.angle.text
def do_calculation(self):
try:
# angle in degrees, convert to radians
force = self.force.text
angle = self.angle.text * (pi / 180)
fx = force * cos(angle)
fy = force * sin(angle)
except TypeError as error:
self.Fx.text = None
self.Fy.text = None
self.do_error('use positive values')
else:
if fx <= 0 or fy <= 0:
self.Fx.text = None
self.Fy.text = None
self.do_error('use positive values')
else:
self.Fx.text = f'{fx:.2f}'
self.Fy.text = f'{fy:.2f}'
self.do_error(None)
def do_error(self, error):
# check for error and display it if present
if error:
self.error.text = error
self.error.visible = True
else:
# hide error and clear it
self.error.text = ""
self.error.visible = False
Tasks
Add a dropdown to specify the number of decimal places in the output values.
Create a force calculator that calculates the force and the angle given the 2 components, Fx and Fy.